Figure 2
Download original image
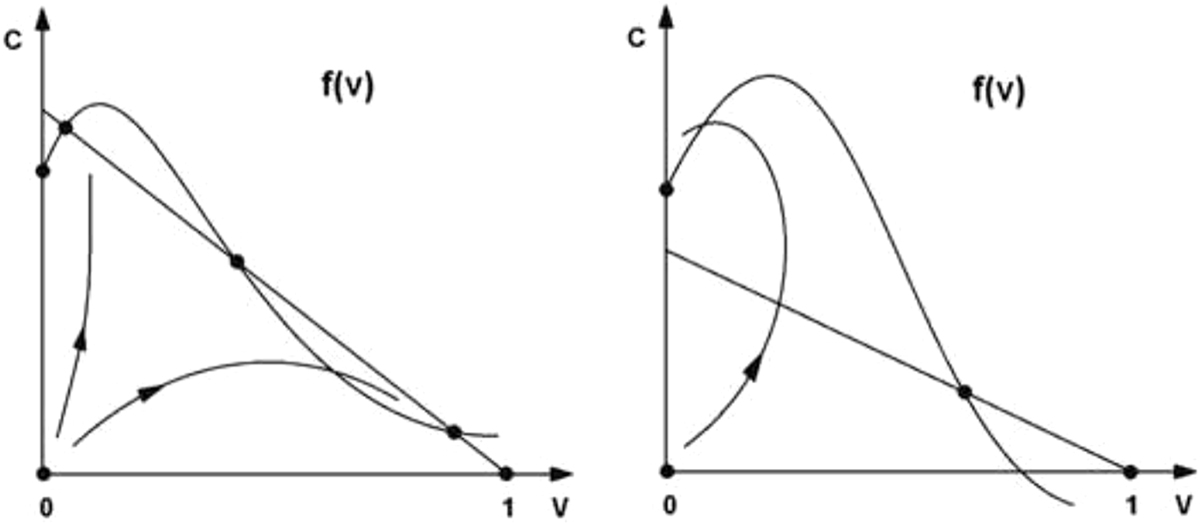
Two examples of phase portrait of system (3.1), (3.2) depending on the function f(v) = 1− h(v)∕p(v). It can have six (left) or four (right) stationary points. The trajectory with the initial condition (v0, c0 ) and sufficiently small viral load v0 can go either to the stationary point with complete virus elimination (right) or to a weak persistent infection (left). If the initial viral load is sufficiently large, then the trajectory approaches the stationary point with large v and small c. It corresponds to a strong chronic infection or to death. Reprinted from [2].
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


